Gas vs Electric Commercial Ovens: Pros & Cons
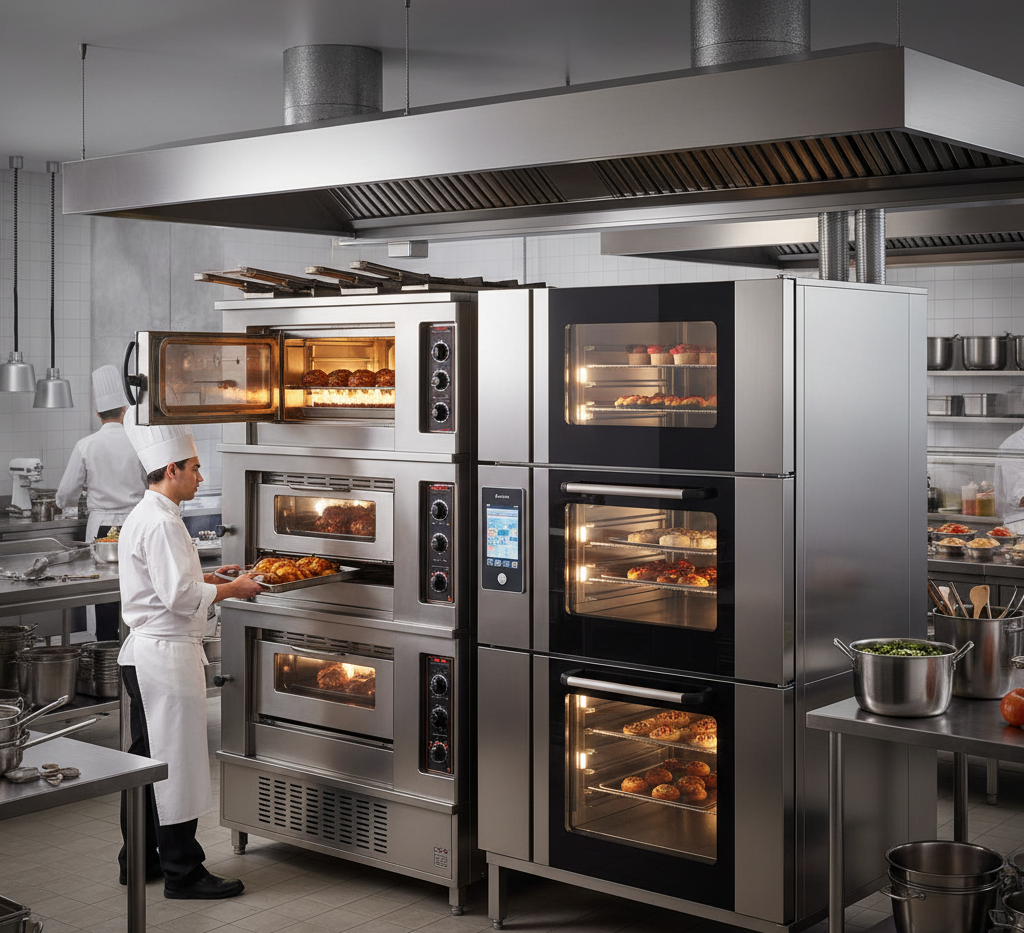

The oven is the centerpiece of any commercial kitchen. It’s where the magic happens, transforming raw ingredients into the delectable dishes that define your business. But when it comes to choosing the right oven, one of the most critical decisions you’ll face is the power source: gas or electric.
Both gas and electric commercial ovens have a long-standing presence in the food service industry, and each comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The “right” choice for your business depends on a variety of factors, including your menu, budget, kitchen layout, and long-term operational goals.
Let’s break down the pros and cons to help you make an informed decision to choose between a Gas and Electric Commercial Oven.
Gas Commercial Ovens
Gas ovens are powered by natural gas or propane and are a popular choice in many commercial kitchens due to their speed and cost-effectiveness.
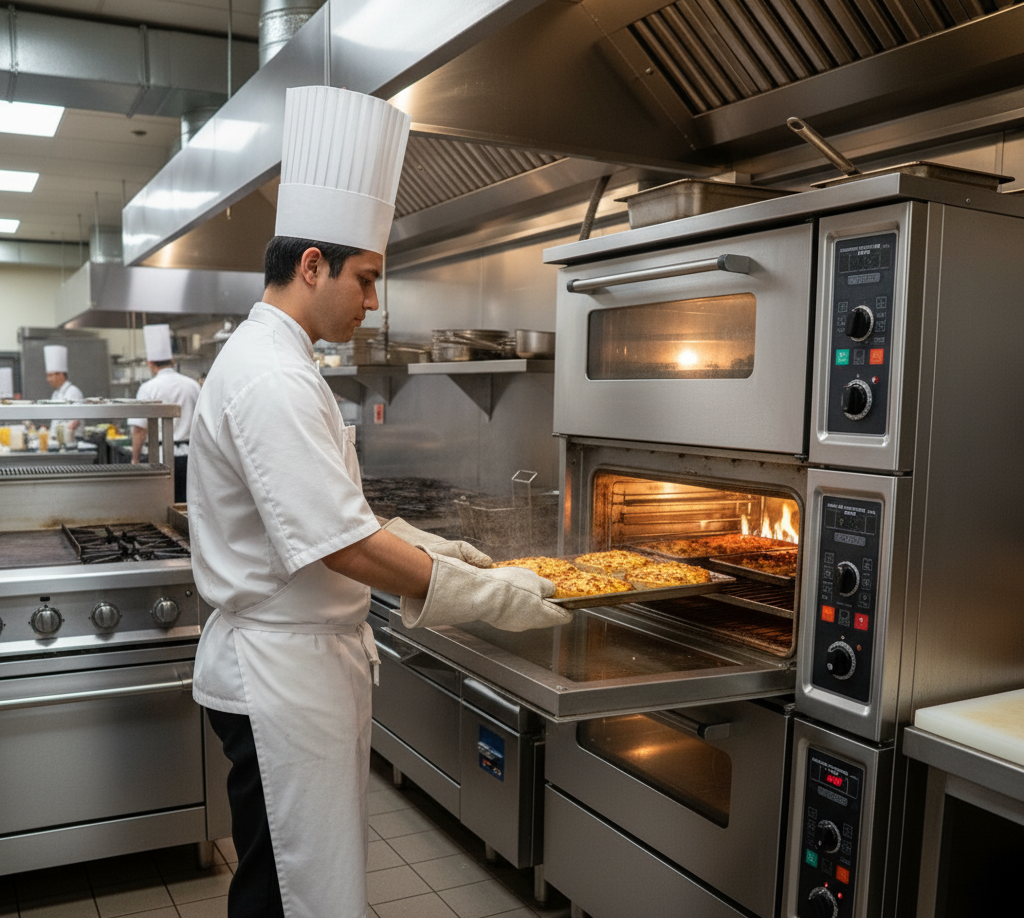

Pros of Gas Ovens
- Faster Heating: Gas ovens heat up quickly, often reaching desired temperatures faster than electric models. This is ideal for high-volume kitchens where speed is critical.
- Lower Operating Costs: In many regions, natural gas is cheaper than electricity, leading to lower utility bills over time, especially in kitchens with heavy oven use.
- Consistent Heat for Baking: Gas ovens provide moist heat, which is beneficial for baking bread, pastries, and other items that require a humid cooking environment.
- Reliability During Power Outages: Gas ovens can often operate during electrical outages, ensuring your kitchen stays functional in emergencies (provided ventilation systems are operational).
- High Heat Output: Gas ovens can achieve very high temperatures, making them suitable for tasks like pizza baking or roasting that require intense heat.
Cons of Gas Ovens
- Higher Initial Cost: Gas ovens often have a higher upfront purchase and installation cost, especially if your kitchen requires gas line installation or modifications.
- Ventilation Requirements: Gas ovens produce combustion byproducts, necessitating proper ventilation systems, which can add to installation and maintenance costs.
- Inconsistent Temperature Control: Some gas ovens may have less precise temperature regulation compared to electric models, which can affect delicate baking tasks.
- Safety Concerns: Gas leaks or improper maintenance can pose safety risks, requiring regular inspections and adherence to safety protocols.
Electric Commercial Ovens
Limited Portability: Gas ovens rely on a fixed gas line, making them less flexible if you need to rearrange or relocate your kitchen.
Electric ovens run on electricity and are known for their precision and versatility, making them a staple in many modern commercial kitchens.
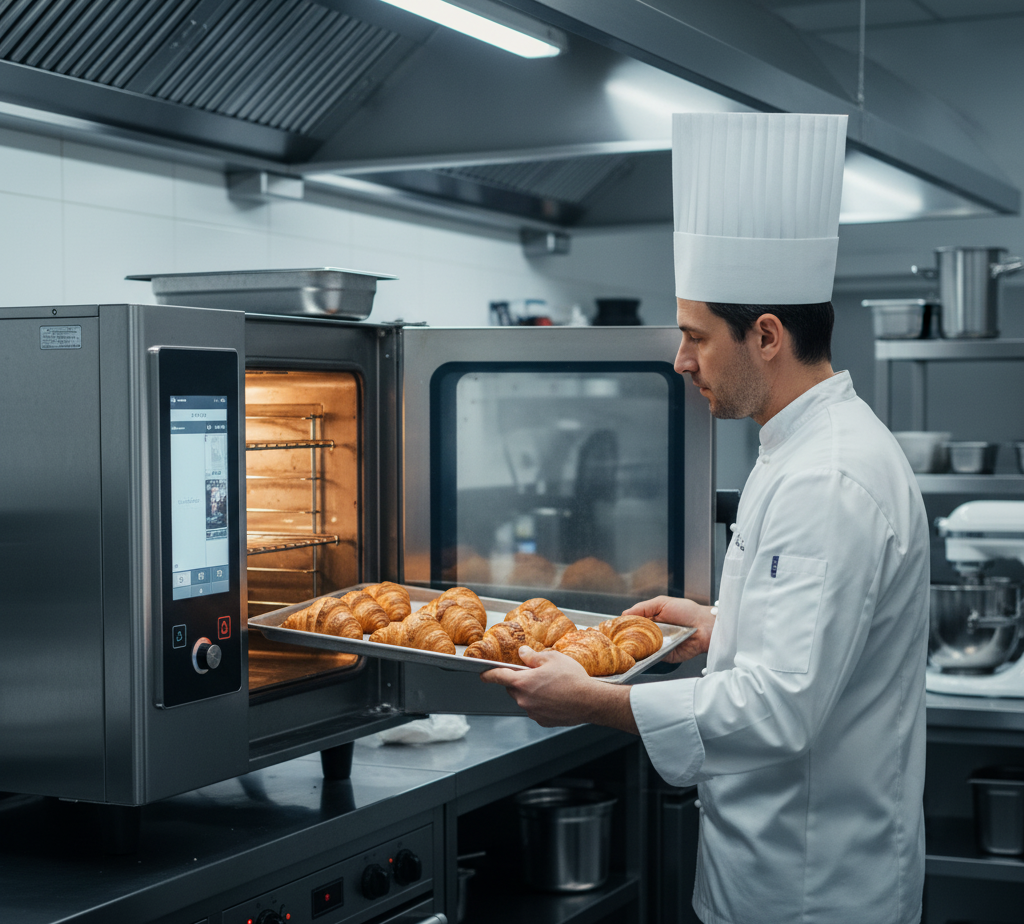

Pros of Electric Ovens
- Precise Temperature Control: Electric ovens offer accurate and consistent temperature regulation, which is ideal for delicate baking, pastries, or recipes requiring exact temperatures.
- Easier Installation: Electric ovens typically require only a power outlet, avoiding the need for gas lines or complex ventilation systems, which can lower installation costs.
- Cleaner Operation: Electric ovens produce no combustion byproducts, eliminating the need for extensive ventilation and reducing indoor air quality concerns.
- Versatility: Many electric ovens come with advanced features like programmable settings, convection fans, and steam functions, enhancing their functionality for diverse cooking needs.
- Safer Operation: Without the risk of gas leaks, electric ovens are generally considered safer, requiring less stringent safety protocols.
Cons of Electric Ovens
- Higher Operating Costs: Electricity is often more expensive than natural gas, leading to higher utility bills, especially in high-output kitchens.
- Slower Heating: Electric ovens may take longer to preheat compared to gas models, which can slow down operations in fast-paced environments.
- Dependence on Electricity: Power outages can render electric ovens unusable, disrupting kitchen operations unless a backup power source is available.
- Dry Heat: Electric ovens tend to produce drier heat, which may not be ideal for certain baking applications like artisan bread that benefit from moisture.
- Capacity Limitations: Some electric ovens may have lower maximum temperatures or capacity compared to gas ovens, potentially limiting their use for high-heat applications.
Key Considerations for Choosing Between Gas and Electric Ovens
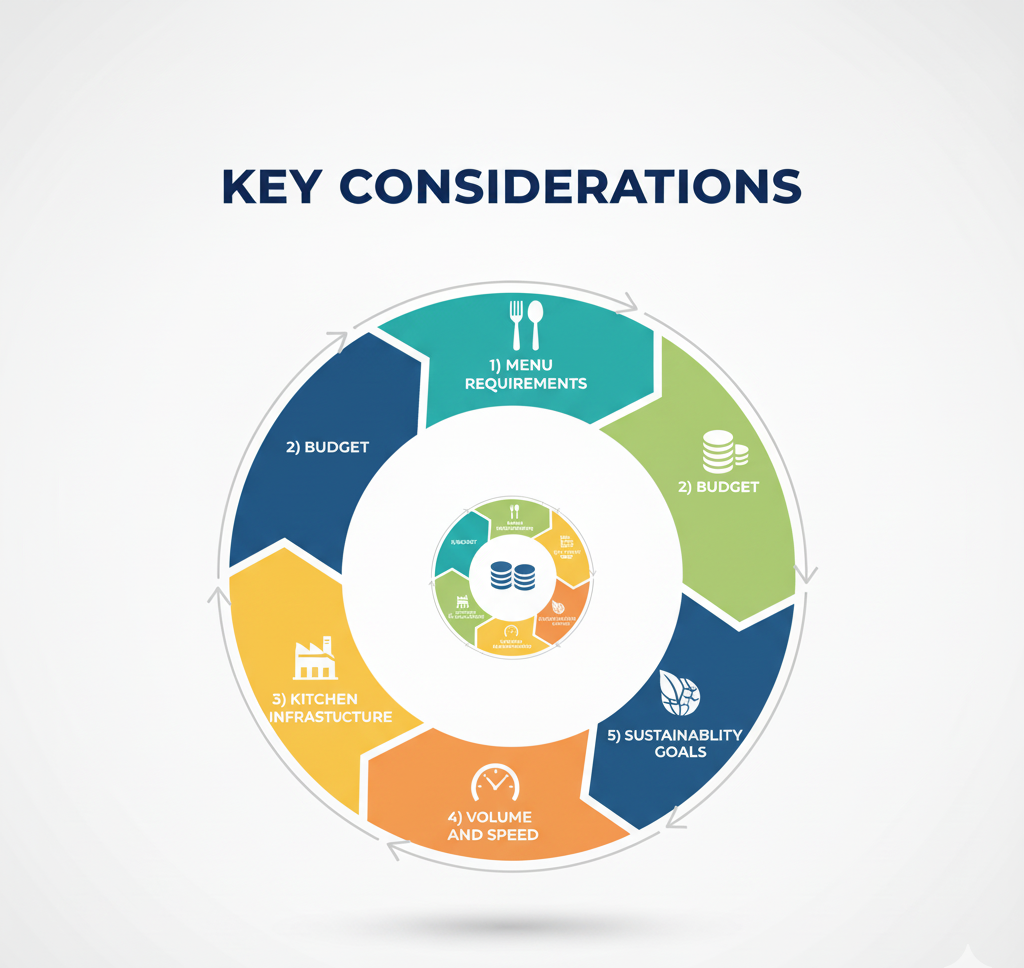
When deciding between gas and electric commercial ovens, consider the following factors:
- Menu Requirements: If your menu focuses on high-heat cooking (e.g., pizzas), a gas oven may be better. For precise baking (e.g., cakes or pastries), an electric oven might be preferable.
- Budget: Factor in both upfront costs (purchase and installation) and long-term operating costs (utilities and maintenance).
- Kitchen Infrastructure: Check if your kitchen has access to a gas line or sufficient electrical capacity. Ventilation requirements for gas ovens can also impact your decision.
- Volume and Speed: High-volume kitchens may benefit from the faster heating of gas ovens, while smaller operations might prioritize the precision of electric ovens.
- Sustainability Goals: Electric ovens may align better with eco-friendly initiatives, especially if paired with renewable energy sources, while gas ovens may have a larger environmental footprint.
Conclusion
Both gas and electric commercial ovens have unique strengths and weaknesses. Gas ovens excel in speed, cost-efficiency, and high-heat applications but require careful maintenance and ventilation. Electric ovens offer precision, ease of installation, and cleaner operation but may come with higher operating costs and slower preheat times. Muskan Equipments Co. sells the best quality gas and electric ovens to meet your commercial kitchen needs. By evaluating your kitchen’s specific needs, budget, and infrastructure, you can choose the oven that best supports your business’s success. For further guidance, consult with equipment suppliers or kitchen design experts to ensure your choice aligns with your operational goals.
